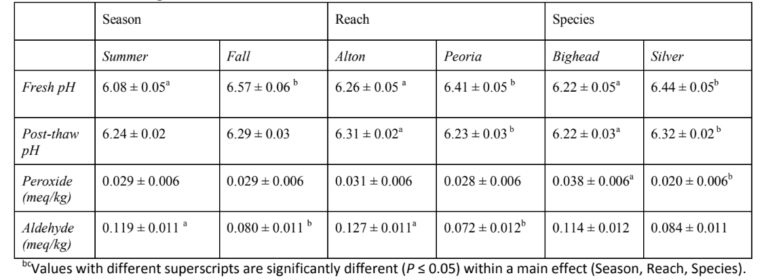
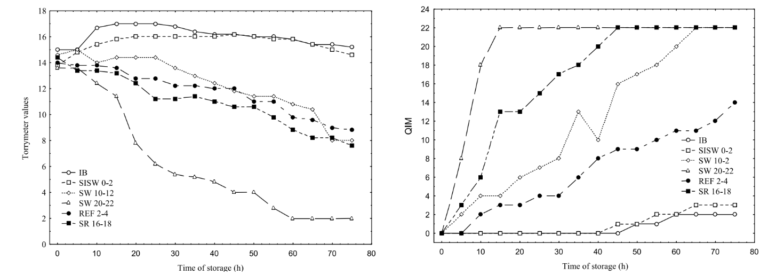
Torrymeter: Safety Evaluation of Fish
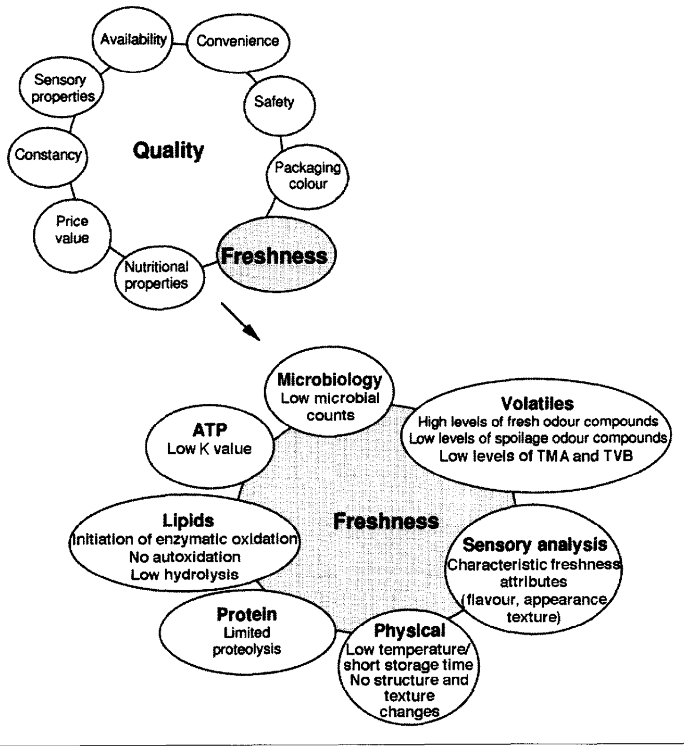
The quality of fish and fishery products is a major concern in fish industry worldwide. Essentially, the objective of fish and fish product assessment is to avoid the ingestion of contaminated food; to evaluate the nutritive value of food by detecting the presence of biological, chemical and physical hazards and in the end to ensure the safety of the consumer. To assess the safety of fish and fish products both instrumental and sensory methods are used. Sensory methods are the most satisfactory way of assessing the spoilage and freshness of fish and fishery products.